GATE 2026 Chemical Engineering Important Questions
GATE 2026 Important Questions in Chemical Engineering-CH Welcome to gatechemical.com - Your Gateway to Success!
Prepare for GATE 2026 with confidence using the expertly curated important questions in Chemical Engineering (CH), analyzed by the distinguished faculty of Engineers Institute of India (EII). Recognized as a benchmark for quality coaching and preparation exclusively for Chemical Engineering, EII is committed to helping you excel in the upcoming GATE examination.
DOWNLOAD GATE-2026 SAMPLE PAPER Practice Set-01
General Aptitude-Based on GATE Pattern
TYPE : MCQ ( Q.1 to Q.5 Carrying 1 Mark each)
Q.1 Which word completes the analogy "Fish is to Shoal as Lion is to _______"?
- (A) Pride
- (B) School
- (C) Forest
- (D) Series
Answer: (A)
Explanation:
Analogies are based on relationships between pairs of words, so we need to determine the specific relationship and apply it consistently.
Step 1: Analyze the Relationship
- Fish and Shoal: A "shoal" is a collective noun for a group of fish that swim together loosely. It describes the social grouping of fish in their natural behavior.
- The relationship is: Fish (individual animal) is part of a Shoal (the collective group of that animal).
Step 2: Apply the Relationship to Lion
- Lion: We need the collective noun that represents a group of lions, similar to how a shoal represents a group of fish.
- Lions are known to live and hunt in social groups. The standard collective noun for a group of lions is a pride.
- Pride: A pride is the correct collective noun for a group of lions, directly analogous to a shoal for fish. Lions form prides, just as fish form shoals.
Q.2 Which sentence is grammatically correct?
- (A) It is I who am responsible for this fiasco.
- (B) It is myself who is responsible for this fiasco.
- (C) It is I who is responsible for this fiasco.
- (D) It is I who are responsible for this fiasco.
Answer: (A)
Explanation:
A - "It is I who am responsible" translates to "I am the one who am responsible," which is grammatically consistent:
- I matches the subjective case.
- am in "who am" agrees with I.
Other options fail:
- B - misuses myself and has is (wrong person).
- C - has is (wrong person for I).
- D - has are (wrong number/person for I).
Q.3 Cars P and Q start from point X in Gurugram at 10 AM. Car P heads North at 25 km/h and travels continuously, while Car Q heads East at 30 km/h but stops after 1 hour. If both are equidistant from X at 11:30 AM, how many minutes did Car Q stop for?
- (A) 10
- (B) 12
- (C) 15
- (D) 18
Answer: (C)
Explanation:
Step 1: Distance by car P at 11:30 AM
- Time: 10:00 AM to 11:30 AM = 1.5 hours.
- Speed: 25 km/h.
- Distance: 25 × 1.5 = 37.5 km.
Step 2: Distance by car Q
- Q travels 1 hour (10:00–11:00 AM) at 30 km/h = 30 km.
- Q stops from 11:00 AM to 11:00 AM + t t t.
- At 11:30 AM, Q’s distance must equal P’s = 37.5 km.
Step 3: Calculate Q’s travel time
- To cover 37.5 km at 30 km/h:
- Time: 37.5 ÷ 30 = 1.25 hours (1 hour 15 minutes).
- Q travels until: 11:15 AM (10:00 AM + 1.25 hours).
Step 4: Find stoppage time
- Q stops from: 11:15 AM to 11:30 AM.
- Stoppage: 11:30 AM – 11:15 AM = 15 minutes.
Q.4 Which statement is NOT true for all real 𝑥 regarding floor and ceiling functions?
- (A) ⌈𝑥⌉ ≥ 𝑥
- (B) ⌊𝑥⌋ ≤ 𝑥
- (C) ⌈𝑥⌉ ≥ ⌊𝑥⌋
- (D) ⌊𝑥⌋ + 1 = ⌈𝑥⌉
Answer: (D)
Explanation:
The ceiling function ⌈x⌉ is the smallest integer ≥ x, and the floor function ⌊x⌋ is the largest integer ≤ x. We need to identify a statement that’s NOT true for all real x.
Common statement to test: ⌊x⌋ + 1 = ⌈x⌉
For x = 2.3:
- ⌊2.3⌋ = 2, 2 + 1 = 3.
- ⌈2.3⌉ = 3, true.
For x = 2:
- ⌊2⌋ = 2, 2 + 1 = 3.
- ⌈2⌉ = 2, false.
The statement ⌊x⌋ + 1 = ⌈x⌉ is NOT correct for all x.
Q.5 P and Q play chess. P wins 80%, draws 15%, and loses 5%. If they play 3 more matches, what is the probability that P wins exactly 2?
- (A) 48/125
- (B) 16/125
- (C) 16/25
- (D) 25/48
Answer: (A)
Explanation:
To find the probability that P wins exactly 2 of 3 chess matches against Q, given P's win rate is 80%, draw rate is 15%, and loss rate is 5%, we use the binomial probability formula. The outcomes are win, draw, or loss, but the question asks for the probability of exactly 2 wins, so we focus on wins versus non-wins.
Q.6 Select the most logical sentence sequence to form a paragraph.
P. At once, without thinking much, people rushed towards the city in hordes with the sole aim of grabbing as much gold as they could.
Q. However, little did they realize about the impending hardships they would have to face on their way to the city: miles of mud, unfriendly forests, hungry beasts and inimical local lords – all of which would reduce their chances of getting gold to almost zero.
R. All of them thought that easily they could lay their hands on gold and become wealthy overnight.
S. About a hundred years ago, the news that gold had been discovered in Kolar spread like wildfire and the whole State was in raptures.
- (A) P → Q → R → S
- (B) Q → S → R → P
- (C) S → Q → P → R
- (D) S → P → R → Q
Answer: (D)
Explanation:
Step 1: Analyze Sentence Connections
- S sets the scene by introducing the gold discovery and public excitement, making it a natural starting point.
- P describes the immediate reaction—people rushing to the city—logically following the news of gold.
- R explains the mindset behind the rush (belief in easy wealth), which aligns with why people acted impulsively in P.
- Q introduces the reality check—hardships that people didn't foresee—serving as a consequence or twist after the optimism in P and R.
Sequence and Flow
- Sequence: Gold discovered, excitement spreads (S); people rush to the city (P); they believe they’ll get rich easily (R); but face unforeseen hardships (Q).
- Flow: S introduces the event, P shows the action, R explains the motivation, and Q provides the consequence (hardships). Logical and cohesive.
Q.7 If HIDE → 19-23-7-11 and CAGE → 5-2-17-11, what is the code for HIGH?
- (A) 5-17-1-2
- (B) 17-19-13-17
- (C) 13-3-1-2
- (D) 19-23-17-19
Answer: (D)
Explanation:
HIDE → 19-23-7-11
CAGE → 5-2-17-11
HIGH ⇒ 19-23-17-19
Q.8 A figure is reflected horizontally and then rotated 90° clockwise. Which is the resulting figure?
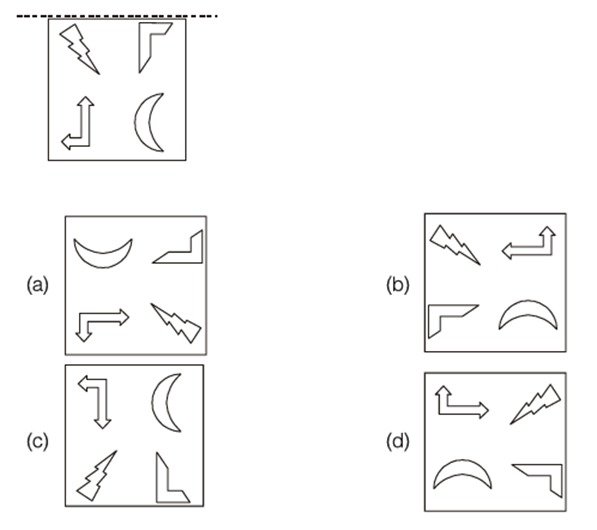
Answer: (Depends on actual figures shown)
Explanation:
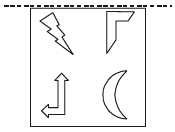
Anti-clockwise figure
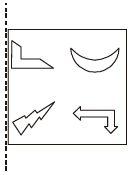
Reflection along horizontal line figure
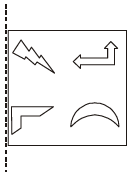
Q.9 Arrange in increasing order of lines of symmetry: Isosceles triangle, Equilateral triangle, Square, Circle.
- (A) Circle; Square; Equilateral triangle; Isosceles triangle
- (B) Isosceles triangle; Equilateral triangle; Square; Circle
- (C) Equilateral triangle; Isosceles triangle; Square; Circle
- (D) Isosceles triangle; Square; Equilateral triangle; Circle
Answer: (B)
Explanation:
The Correct Sequence of Objects Based on Increasing Number of Mirror Lines (Lines of Symmetry)
- Isosceles Triangle: It has 1 line of symmetry.
- Equilateral Triangle: It has 3 lines of symmetry.
- Square: It has 4 lines of symmetry.
- Circle: It has infinite lines of symmetry, as any line passing through the center is a line of symmetry.
Q.10 A student has 0.8 and 0.6 probability of job offers from Company S and T respectively. What is the probability of getting both?
- (A) 0 ≤ p ≤ 0.2
- (B) 0.4 ≤ p ≤ 0.6
- (C) 0.2 ≤ p ≤ 0.4
- (D) 0.6 ≤ p ≤ 1.0
Answer: (B)
Explanation: P (S) = 0.8 P (T) = 0.6 P (S∩T) = P (S) . P (T) = (0.8) . (0.6) = 0.48
Fundamentals & Theory | Important-Questions Set 01
Exp : In forced convection, fans or pumps induce higher fluid velocities, leading to thinner thermal boundary layers and greater turbulence, which enhances convective heat transfer significantly.
- GATE 2026 Heat Transfer-HT : Basics Fundamentals Practice 01
- GATE 2026 Heat Transfer-HT : Basics Fundamentals Practice 02
- GATE 2026 Heat Transfer-HT : Basics Fundamentals Practice 03
- GATE 2026 Heat Transfer-HT : Numerical Based Practice 01
- GATE 2026 Heat Transfer-HT : Numerical Based Practice 02
- GATE 2026 Heat Transfer-HT : Numerical Based Practice 03
TYPE : MCQ Basic Level (Q.1–Q.15)
1. In molecular diffusion, the driving force is governed by:
2. Fick’s second law applies to:
3. The diffusion coefficient (D) in Fick’s law depends on:
4. In a binary mixture, molecular diffusion is enhanced by:
5. The mass transfer coefficient (k) is defined as:
6. Film theory assumes mass transfer occurs through:
7. Penetration theory is based on:
8. Surface renewal theory differs from film theory by:
9. The Chilton-Colburn analogy relates:
10. In stage-wise contacting, the efficiency is affected by:
11. Continuous contacting is characterized by:
12. The stage efficiency in a distillation column is:
13. HTU (Height of Transfer Unit) is used to:
14. NTU (Number of Transfer Units) indicates:
15. Distillation equipment design considers:
TYPE : MCQ Intermediate Level (Q.16-Q.30)
16. Absorption equipment operates on the principle of:
17. Leaching process efficiency depends on:
18. Liquid-liquid extraction requires:
19. Drying equipment design focuses on:
20. Humidification is achieved by:
21. Dehumidification involves:
22. Adsorption process depends on:
23. Micro-filtration separates:
24. Ultra-filtration is effective for:
25. Nano-filtration targets:
26. Reverse osmosis is used for:
27. The Sherwood number (Sh) relates to:
28. In a distillation column, equilibrium stage achievement depends on:
29. HTU decreases with:
30. NTU increases with:
- GATE 2026 Mass Transfer-MT: Basics Fundamentals Practice 01
- GATE 2026 Mass Transfer-MT: Basics Fundamentals Practice 02
- GATE 2026 Mass Transfer-MT: Basics Fundamentals Practice 03
- GATE 2026 Mass Transfer-MT: Numerical Based Practice 01
- GATE 2026 Mass Transfer-MT: Numerical Based Practice 02
- GATE 2026 Mass Transfer-MT: Numerical Based Practice 03
1. The first law of thermodynamics is based on the principle of:
- A) Conservation of mass
- B) Conservation of energy
- C) Conservation of entropy
- D) Conservation of momentum
Answer: B
Explanation: The first law states that the change in internal energy of a system is equal to the heat added minus the work done, embodying energy conservation.
2. For a closed system, the first law can be expressed as:
- A) ΔU = Q - W
- B) ΔH = Q + W
- C) ΔS = Q/T
- D) ΔG = ΔH - TΔS
Answer: A
Explanation: For a closed system, ΔU = Q - W, where ΔU is the change in internal energy, Q is heat added, and W is work done by the system.
3. In an open system, the first law includes:
- A) Only heat and work
- B) Mass flow terms
- C) Entropy change
- D) Gibbs free energy
Answer: B
Explanation: The first law for an open system includes mass flow terms (enthalpy of inlet and outlet streams) in addition to heat and work.
4. The second law of thermodynamics introduces the concept of:
- A) Energy
- B) Entropy
- C) Pressure
- D) Volume
Answer: B
Explanation: The second law states that the entropy of an isolated system always increases, introducing the concept of entropy as a measure of disorder.
5. A process with zero entropy change is:
- A) Irreversible
- B) Reversible
- C) Adiabatic
- D) Isothermal
Answer: B
Explanation: A reversible process occurs with no net entropy change, assuming ideal conditions with no irreversibilities.
6. The entropy change for an ideal gas undergoing isothermal expansion is given by:
- A) ΔS = 0
- B) ΔS = nR ln(V₂/V₁)
- C) ΔS = nCv ln(T₂/T₁)
- D) ΔS = nCp ln(P₂/P₁)
Answer: B
Explanation: For an ideal gas in isothermal expansion, ΔS = nR ln(V₂/V₁), where volume increases, leading to increased entropy.
7. The equation of state for an ideal gas is:
- A) PV = nRT
- B) P + a/V² = nRT
- C) (P + a/V²)(V - b) = nRT
- D) PVᵞ = constant
Answer: A
Explanation: The ideal gas law, PV = nRT, relates pressure, volume, and temperature for an ideal gas.
8. Residual properties are defined as:
- A) Properties of pure substances
- B) Difference between real and ideal gas properties
- C) Properties at constant entropy
- D) Properties of mixtures
Answer: B
Explanation: Residual properties account for the deviation of real gas behavior from ideal gas behavior using equations like the virial equation.
9. The partial molar property of a component in a mixture is:
- A) The total property of the mixture
- B) The property change with respect to the mole fraction of that component
- C) The entropy of the mixture
- D) The heat capacity of the component
Answer: B
Explanation: Partial molar property is the change in the extensive property of a mixture with the addition of one mole of the component, keeping other mole fractions constant.
10. Fugacity is a measure of:
- A) Ideal gas behavior
- B) Effective pressure accounting for non-ideality
- C) Entropy change
- D) Heat transfer
Answer: B
Explanation: Fugacity is an effective pressure that corrects for non-ideal behavior in real gases and mixtures.
11. Excess properties are related to:
- A) Ideal mixture behavior
- B) Deviation from ideal mixture behavior
- C) Pure substance properties
- D) Adiabatic processes
Answer: B
Explanation: Excess properties represent the deviation of a real mixture’s properties from those of an ideal mixture.
12. Activity coefficients are used to:
- A) Calculate ideal gas properties
- B) Account for non-ideal behavior in liquid mixtures
- C) Determine entropy changes
- D) Measure heat capacity
Answer: B
Explanation: Activity coefficients correct for non-ideal interactions in liquid mixtures, affecting phase equilibria.
13. Phase equilibrium for vapor-liquid systems is predicted using:
- A) Gibbs phase rule
- B) Raoult’s law
- C) Newton’s law
- D) Fourier’s law
Answer: B
Explanation: Raoult’s law predicts VLE by assuming the partial pressure of each component is proportional to its mole fraction in the liquid phase.
14. Chemical reaction equilibrium is governed by:
- A) First law of thermodynamics
- B) Second law of thermodynamics
- C) Gibbs free energy minimization
- D) Entropy maximization
Answer: C
Explanation: At equilibrium, a chemical reaction minimizes Gibbs free energy (ΔG = 0) under constant temperature and pressure.
15. For a closed system with no work done, the first law simplifies to:
- A) ΔU = Q
- B) ΔH = 0
- C) ΔS = 0
- D) ΔG = 0
Answer: A
Explanation: If no work is done (W = 0), the first law becomes ΔU = Q for a closed system, where ΔU is the change in internal energy and Q is the heat added to the system.
16. The entropy change for an irreversible process is:
- A) Zero
- B) Positive
- C) Negative
- D) Constant
Answer: B
Explanation: The second law of thermodynamics states that for an irreversible process, the entropy increases, indicating a positive change in entropy.
17. In an open system, the steady-state energy balance includes:
- A) Only internal energy
- B) Enthalpy flow and heat transfer
- C) Entropy flow
- D) Work done by friction
Answer: B
Explanation: In a steady-state energy balance, both enthalpy flow due to mass transfer and heat transfer are considered, with accumulation typically neglected.
18. The Clausius inequality relates to:
- A) Energy conservation
- B) Entropy increase in irreversible cycles
- C) Heat transfer coefficient
- D) Mass transfer rate
Answer: B
Explanation: The Clausius inequality (∫δQ/T ≤ 0) describes the entropy change for irreversible processes, indicating entropy increase in irreversible cycles.
19. The compressibility factor (Z) for a real gas is:
- A) Always 1
- B) PV/nRT
- C) Depends on pressure and temperature
- D) Zero for ideal gases
Answer: C
Explanation: The compressibility factor Z = PV/nRT quantifies the deviation of a real gas from ideal gas behavior. It depends on both pressure and temperature.
20. Partial molar enthalpy of a mixture component is:
- A) The total enthalpy
- B) The enthalpy change with mole fraction
- C) The heat of reaction
- D) The entropy change
Answer: B
Explanation: Partial molar enthalpy is the change in the enthalpy of a mixture due to the addition of one mole of a component, keeping the mole fractions of other components constant.
21. The fugacity coefficient approaches 1 for:
- A) High pressures
- B) Ideal gases
- C) Low temperatures
- D) Real liquids
Answer: B
Explanation: Fugacity coefficient equals 1 for ideal gases where non-ideal effects are negligible.
22. Excess Gibbs free energy is zero for:
- A) Real mixtures
- B) Ideal mixtures
- C) Non-ideal gases
- D) Pure substances
Answer: B
Explanation: Excess Gibbs free energy is zero for ideal mixtures where intermolecular interactions are absent.
23. VLE prediction using activity coefficients requires:
- A) Ideal gas law
- B) Non-ideal solution models
- C) Constant pressure
- D) No temperature effect
Answer: B
Explanation: Activity coefficients account for non-ideal behavior in liquid phases for accurate VLE prediction.
24. Chemical equilibrium constant (K) is related to:
- A) Entropy change
- B) Gibbs free energy change
- C) Enthalpy change
- D) Internal energy
Answer: B
Explanation: K = exp(-ΔG°/RT), where ΔG° is the standard Gibbs free energy change.
25. For a reversible adiabatic process, entropy change is:
- A) Positive
- B) Negative
- C) Zero
- D) Infinite
Answer: C
Explanation: In a reversible adiabatic process (Q = 0), entropy change is zero due to no heat transfer.
26. The first law application to a turbine involves:
- A) Only work output
- B) Enthalpy drop and work
- C) Entropy increase
- D) Heat input
Answer: B
Explanation: The first law for a turbine relates the enthalpy drop across the turbine to the work output.
27. The second law efficiency is defined as:
- A) Work output/Heat input
- B) Actual entropy change/Ideal entropy change
- C) Reversible work/Actual work
- D) Heat transfer rate
Answer: C
Explanation: Second law efficiency is the ratio of reversible work to actual work, indicating process perfection.
28. Residual enthalpy depends on:
- A) Ideal gas properties
- B) Real gas deviations
- C) Constant volume
- D) Temperature only
Answer: B
Explanation: Residual enthalpy accounts for deviations of real gas behavior from ideal gas properties.
29. The activity coefficient of an ideal solution is:
- A) Zero
- B) One
- C) Infinite
- D) Negative
Answer: B
Explanation: In an ideal solution, activity coefficients are 1 due to no deviation from Raoult’s law.
30. In GATE 2023, a question on entropy change for an ideal gas matched with:
- A) Isothermal process
- B) Adiabatic process
- C) Polytropic process
- D) Isobaric process
Answer: A
Explanation: GATE 2023 included a problem on entropy change (ΔS = nR ln(V₂/V₁)) for an ideal gas in isothermal expansion.
31. In GATE 2022, a problem on first law for an open system involved:
- A) Only heat transfer
- B) Enthalpy balance with mass flow
- C) Entropy balance
- D) Work only
Answer: B
Explanation: GATE 2022 featured an open system energy balance with enthalpy flow terms, matching practical applications.
32. GATE 2021 tested the second law with:
- A) Entropy increase in a cycle
- B) Energy conservation
- C) Heat transfer coefficient
- D) Mass transfer rate
Answer: A
Explanation: A GATE 2021 question involved entropy increase in an irreversible cycle, aligning with second law principles.
33. A GATE 2023 question on equation of state involved:
- A) Ideal gas law
- B) Van der Waals equation
- C) Bernoulli equation
- D) Continuity equation
Answer: B
Explanation: GATE 2023 included a problem using the Van der Waals equation for real gas behavior.
34. GATE 2024 tested partial molar properties in:
- A) Pure substances
- B) Binary mixtures
- C) Ternary systems
- D) Ideal gases
Answer: B
Explanation: A GATE 2024 question calculated partial molar volume in a binary mixture.
35. Fugacity was a focus in GATE 2025 with:
- A) Ideal gas
- B) Real gas at high pressure
- C) Liquid mixtures
- D) Constant entropy
Answer: B
Explanation: GATE 2025 featured a fugacity calculation for a real gas under high pressure conditions.
36. GATE 2022 included VLE prediction using:
- A) Dalton’s law
- B) Raoult’s law
- C) Henry’s law
- D) Gibbs-Duhem equation
Answer: B
Explanation: A GATE 2022 problem used Raoult’s law to predict VLE for an ideal system.
37. Chemical equilibrium in GATE 2023 involved:
- A) Enthalpy balance
- B) Gibbs free energy minimization
- C) Entropy maximization
- D) Heat transfer
Answer: B
Explanation: GATE 2023 tested chemical equilibrium using Gibbs free energy minimization.
38. GATE 2024 questioned entropy change for:
- A) Isothermal expansion
- B) Adiabatic compression
- C) Isobaric cooling
- D) Isochoric heating
Answer: A
Explanation: A GATE 2024 problem calculated entropy change for an ideal gas in isothermal expansion.
39. GATE 2021 tested residual properties for:
- A) Ideal mixtures
- B) Real gases
- C) Pure liquids
- D) Solid phases
Answer: B
Explanation: GATE 2021 included a residual enthalpy calculation for a real gas.
40. Activity coefficients appeared in GATE 2025 for:
- A) Ideal solutions
- B) Non-ideal liquid mixtures
- C) Gas phases
- D) Solid solutions
Answer: B
Explanation: GATE 2025 featured activity coefficients to account for non-ideal behavior in liquid mixtures.
- GATE 2026 Thermodynamics-Thermo: Basics Fundamentals Practice 01
- GATE 2026 Thermodynamics-Thermo: Basics Fundamentals Practice 02
- GATE 2026 Thermodynamics-Thermo: Basics Fundamentals Practice 03
- GATE 2026 Thermodynamics-Thermo: Numerical Based Practice 01
- GATE 2026 Thermodynamics-Thermo: Numerical Based Practice 02
- GATE 2026 Thermodynamics-Thermo: Numerical Based Practice 03
Basic Level (1–10)
Intermediate Level (11–25)
11. What is the pressure difference (in Pa) due to surface tension in a 1 mm diameter water droplet (σ = 0.073 N/m)?
- A) 146
- B) 73
- C) 292
- D) 36.5
Answer: A
Explanation: ΔP = 4σ/d = 4 × 0.073 / 0.001 = 146 Pa.
12. A non-Newtonian fluid exhibits:
- A) Constant viscosity
- B) Shear-thinning behavior
- C) Linear stress-strain
- D) Zero viscosity
Answer: B
Explanation: Non-Newtonian fluids like pseudoplastics show viscosity decreasing with shear rate.
13. The Navier-Stokes equation represents:
- A) Energy balance
- B) Momentum balance
- C) Mass balance
- D) Friction factor
Answer: B
Explanation: It’s the differential form of momentum conservation.
14. In turbulent flow, friction factor depends on:
- A) Reynolds number only
- B) Pipe roughness and Re
- C) Fluid viscosity only
- D) Pipe length
Answer: B
Explanation: Turbulent f is a function of Re and relative roughness (Moody chart).
15. The Buckingham Pi theorem determines:
- A) Flow velocity
- B) Number of dimensionless groups
- C) Pressure drop
- D) Pipe diameter
Answer: B
Explanation: It calculates π terms as variables minus dimensions.
16. For laminar flow in a pipe, pressure drop is proportional to:
- A) Velocity squared
- B) Velocity
- C) Pipe diameter
- D) Fluid density
Answer: B
Explanation: ΔP = (32μLv)/D² from Hagen-Poiseuille.
17. Orifice meters are less accurate than Venturi meters due to:
- A) Higher energy loss
- B) Lower cost
- C) Smaller size
- D) Simpler design
Answer: A
Explanation: Orifice plates cause more permanent pressure loss.
18. The boundary layer thickness increases with:
- A) Decreasing velocity
- B) Increasing distance
- C) Decreasing viscosity
- D) Increasing density
Answer: B
Explanation: δ ∝ √x in laminar boundary layers.
19. Drag force on a sphere in Stokes’ regime is proportional to:
- A) Velocity squared
- B) Velocity
- C) Diameter squared
- D) Density
Answer: B
Explanation: Fd = 6πμrv (Stokes’ law).
20. In a packed bed, pressure drop follows:
- A) Darcy’s law
- B) Ergun equation
- C) Bernoulli equation
- D) Hagen-Poiseuille
Answer: B
Explanation: Ergun accounts for both viscous and inertial losses.
21. The power law index (n) for a shear-thinning fluid is:
- A) n > 1
- B) n = 1
- C) n < 1
- D) n = 0
Answer: C
Explanation: Shear-thinning fluids have n < 1 in τ = K(γ̇)n.
22. The mechanical energy equation includes losses due to:
- A) Friction
- B) Elevation
- C) Velocity
- D) All of the above
Answer: D
Explanation: It balances kinetic, potential, and frictional losses.
23. In turbulent flow, the universal velocity profile shows:
- A) Linear region near wall
- B) Logarithmic region
- C) Parabolic shape
- D) Constant velocity
Answer: B
Explanation: The log-law region dominates in turbulent flow.
24. Minimum fluidization velocity depends on:
- A) Particle size and density
- B) Fluid viscosity only
- C) Pipe diameter
- D) Flow rate
Answer: A
Explanation: Vmf is derived from force balance (Ergun equation).
25. Pressure drop in turbulent flow is proportional to:
- A) Velocity
- B) Velocity squared
- C) Pipe length squared
- D) Fluid viscosity
Answer: B
Explanation: ΔP ∝ v² in turbulent flow (Darcy-Weisbach).
TYPE : MCQ Basic Level (Q.1–Q15)
1. What is the primary factor determining particle shape?
2. Which instrument is commonly used to measure particle size distribution?
3. What is the purpose of size reduction in mechanical operations?
4. Which law governs energy required for size reduction?
5. What is free settling?
6. What is the main force in a centrifuge?
7. Cyclones primarily separate particles based on:
8. What is the purpose of thickening?
9. Filtration separates:
10. What drives agitation in mixing?
11. Which equipment is used for conveying solids?
12. Particle size is typically measured in:
13. What is hindered settling?
14. The efficiency of a cyclone depends on:
15. What is the primary goal of classification?
TYPE : Intermediate Level (Q.16–Q.25)
16. Which method is best for fine particle size analysis?
17. Kick’s Law applies to:
18. Stokes’ Law is used to calculate:
19. What enhances centrifuge separation?
20. In thickening, underflow refers to:
21. Cake filtration occurs when:
22. Which impeller is best for high-viscosity mixing?
23. Pneumatic conveying uses:
24. Screen effectiveness depends on:
25. What reduces settling velocity in hindered settling?
- GATE 2026 Mechanical Operations-MO: Basics Fundamentals Practice 01
- GATE 2026 Mechanical Operations-MO: Basics Fundamentals Practice 02
- GATE 2026 Mechanical Operations-MO: Basics Fundamentals Practice 03
- GATE 2026 Mechanical Operations-MO: Numerical Based Practice 01
- GATE 2026 Mechanical Operations-MO: Numerical Based Practice 02
- GATE 2026 Mechanical Operations-MO: Numerical Based Practice 03
TYPE : GATE-Matched MCQ Questions (Q.1–Q.10)
1. In a steady-state process, the accumulation term in a mass balance equation is:
2. A system with two phases and two components is in equilibrium. According to Gibbs’ phase rule, the degrees of freedom are:
3. The main purpose of a tie component in mass balance calculations is to:
4. In a process, 100 kg/h of feed is split into 60 kg/h recycle and 40 kg/h product. What is the recycle ratio?
5. Which of the following statements is true about an unsteady-state system?
6. In a non-reacting distillation process with a bypass stream, the overall mass balance must include:
7. Which term accounts for the mass that is not part of the main process stream and returns for further processing?
8. In a multiphase system with 3 components and 2 phases, how many degrees of freedom are there (at equilibrium)?
9. Which process balance is more suitable for analyzing combustion reactions?
10. In a chemical process, if a purge stream is removed, what could potentially accumulate in the system?
TYPE : Basics Theoretical MCQ Questions (Q.11–Q.25)
11. Which of the following is NOT a component of a general mass balance equation?
12. What is the degree of freedom for a single-phase binary mixture at constant temperature and pressure?
13. A process stream contains a non-volatile solute and water. Which is the tie component during evaporation?
14. Which of the following represents a closed system?
15. The use of bypass stream is advantageous when:
16. The presence of an inert component in a chemical reaction system:
17. The steady-state energy balance does not include which of the following?
18. In which case would a purge stream be absolutely necessary?
19. Gibb’s phase rule can be applied to:
20. The main purpose of mass transfer operations is:
21. The principle behind a distillation column is based on:
22. Which of the following represents the correct order of stages in a distillation process?
23. The velocity at which a particle settles in a liquid depends on:
24. The main disadvantage of using a batch reactor as compared to a continuous reactor is:
25. Which of the following best describes an isothermal process?
- GATE 2026 Process Calculations-PC: Basics Fundamentals Practice 01
- GATE 2026 Process Calculations-PC: Basics Fundamentals Practice 02
- GATE 2026 Process Calculations-PC: Basics Fundamentals Practice 03
- GATE 2026 Process Calculations-PC: Numerical Based Practice 01
- GATE 2026 Process Calculations-PC: Numerical Based Practice 02
- GATE 2026 Process Calculations-PC: Numerical Based Practice 03
1. The rate of a chemical reaction is defined as:
2. For the reaction sequence A→B→C, maximum yield of B is obtained by:
3. Which of the following reactors assumes perfect mixing?
4. Which of the following is NOT a characteristic of an elementary reaction?
5. The half-life of a first-order reaction is:
6. Enzyme kinetics follow Michaelis-Menten behavior when:
7. In a PFR with constant density and steady-state conditions, the conversion increases:
8. In Michaelis-Menten enzyme kinetics, at very high substrate concentration, the reaction rate becomes:
9. A second-order reaction A → products follows the rate law:
10. (GATE 2022) For a first-order irreversible reaction in a PFR, the relation between conversion (X) and reactor volume (V) is:
11. (GATE 2021) In the context of catalyst deactivation, which statement is true?
12. (GATE 2020) The residence time distribution (RTD) function E(t) for an ideal CSTR is:
13. Non-isothermal reactors need energy balance due to:
14. The selectivity in a multiple reaction system is defined as:
15. In heterogeneous catalysis, the rate-determining step can be:
16. The Thiele modulus is used in:
17. The conversion in an adiabatic reactor is limited by:
18. The effectiveness factor (η) is defined as:
19. The Monod model is used to describe:
20. In an isothermal PFR, conversion increases with:
GATE Pattern Questions (2020–2025)
21. (GATE 2023) For a zero-order reaction, the rate of reaction is:
22. (GATE 2024) The integral method of analyzing kinetic data is useful for:
23. (GATE 2021) The RTD curve for ideal plug flow is:
24. (GATE 2022) Conversion in a batch reactor is found by integrating:
25. (GATE 2020) Catalyst deactivation due to coking is:
Frequently Asked Questions-PSUs
26. A catalyst increases the rate of reaction by:
27. An ideal batch reactor is best suited for:
28. Which model is used for non-ideal reactors?
29. Catalyst surface area plays a crucial role in:
30. For an elementary reaction, the order of the reaction is:
- GATE 2026 Chemical Reaction Engineering-CRE: Basics Fundamentals Practice 01
- GATE 2026 Chemical Reaction Engineering-CRE: Basics Fundamentals Practice 02
- GATE 2026 Chemical Reaction Engineering-CRE: Basics Fundamentals Practice 03
- GATE 2026 Chemical Reaction Engineering-CRE: Numerical Based Practice 01
- GATE 2026 Chemical Reaction Engineering-CRE: Numerical Based Practice 02
- GATE 2026 Chemical Reaction Engineering-CRE: Numerical Based Practice 03
TYPE : MCQ Basic Level (Q.1-Q.15)
1. What is the primary function of a transducer in a process control system?
2. Which sensor is most suitable for measuring temperature in a high-temperature furnace?
3. What does a strain gauge primarily measure?
4. Which of the following is NOT a characteristic of a good sensor?
5. In a P&ID diagram, what does the symbol for a valve with a diamond shape represent?
6. What does the abbreviation "FI" stand for in a P&ID diagram?
7. Which symbol is used to represent a pump in a P&ID diagram?
8. What is the purpose of linearization in process modeling?
9. A first-order process model is characterized by which of the following?
10. What is the transfer function of a pure dead-time process?
11. The transfer function of a system relates:
12. What is the steady-state gain of a first-order system with transfer function K/(τs+1) ?
13. A system with inverse response is characterized by:
14. The process reaction curve method is used to determine:
15. What is the dead time in a process reaction curve?
TYPE : MCQ Intermediate Level (Q.16-Q.25)
16. Which controller mode eliminates steady-state offset in a control system?
17. What is the primary role of the derivative term in a PID controller?
18. A proportional-only controller is likely to result in:
19. What is the function of a control valve in a process control system?
20. Which characteristic of a control valve is preferred for fast-responding processes?
21. The dynamics of a transducer can often be modeled as:
22. What affects the response time of a transducer?
23. The stability of a closed-loop system is determined by:
24. In frequency response analysis, the gain margin indicates:
25. Which tuning method uses the ultimate gain and ultimate period of a system?
- GATE 2026 Instrumentation and Process Control-IPC: Basics Fundamentals Practice 02
- GATE 2026 Instrumentation and Process Control-IPC: Basics Fundamentals Practice 03
- GATE 2026 Instrumentation and Process Control-IPC: Numerical Based Practice 01
- GATE 2026 Instrumentation and Process Control-IPC: Numerical Based Practice 02
- GATE 2026 Instrumentation and Process Control-IPC: Numerical Based Practice 03
TYPE : MCQ Basic Level (Q.1-Q.15)
1. Which of the following is a fixed cost in a chemical plant?
2. The Chemical Engineering Plant Cost Index (CEPCI) in 2020 was 600, and in 2025, it is 720. If a plant cost $1,000,000 in 2020, what is its estimated cost in 2025?
3. The straight-line depreciation method assumes:
4. A machine costs $100,000 with a salvage value of $10,000 and a useful life of 10 years. Using straight-line depreciation, what is the annual depreciation expense?
5. A plant has a capital cost of $500,000, annualized over 5 years at 10% interest, and annual operating costs of $50,000. Using the capital recovery factor, what is the total annualized cost? (Capital recovery factor for 5 years at 10% is 0.2638)
6. The cost of a heat exchanger in 2023 was $50,000 when the CEPCI was 650. If the CEPCI in 2025 is 715, what is the cost in 2025?
7. The internal rate of return (IRR) is the discount rate at which:
8. A project requires an initial investment of $200,000 and generates $60,000 annually for 5 years. If the IRR is approximately 10% (NPV ≈ 0), what is the NPV at a discount rate of 8%? (Present value factor for 5 years at 8% is 3.9927)
9. The payback period is defined as:
10. A project costs $300,000 and generates $100,000 per year. What is the payback period?
11. The profitability index (PI) is defined as:
12. A project has a PI of 1.2. What does this indicate?
13. Which method does NOT consider the time value of money?
14. In capital budgeting, sunk cost is:
15. Break-even point occurs when:
Estimated Weightage for Plant Design and Economics: 4–6 marks (5–8% of total marks)
Typically, 2–3 questions are expected:
1–2 questions (1 mark each): Conceptual questions on topics like cost estimation, depreciation, or payback period.
1 question (2 marks): Calculation-based question involving total annualized cost, discounted cash flow, or equipment sizing (e.g., heat exchangers).
- GATE 2026 Plant Design and Economics-PDE: Basics Fundamentals Practice 02
- GATE 2026 Plant Design and Economics-PDE: Basics Fundamentals Practice 03
- GATE 2026 Plant Design and Economics-PDE: Numerical Based Practice 01
- GATE 2026 Plant Design and Economics-PDE: Numerical Based Practice 02
- GATE 2026 Plant Design and Economics-PDE: Numerical Based Practice 03
TYPE : MCQ Basic Level (Q.1-Q.20)
1. Sulfuric Acid Production: In the contact process for sulfuric acid production, the catalyst used is:
2. Sulfuric Acid Process: The primary purpose of the absorption tower in the contact process is to:
3. Phosphoric Acid Production: The wet process for phosphoric acid production involves the reaction of phosphate rock with:
4. Chlor-Alkali Industry: In the chlor-alkali process, which product is formed at the cathode in the diaphragm cell?
5. Chlor-Alkali Industry: The membrane cell process in the chlor-alkali industry uses a membrane made of:
6. Ammonia Production: The Haber-Bosch process for ammonia synthesis operates at:
7. Ammonia Synthesis: The catalyst used in the Haber-Bosch process is:
8. Urea Production: Urea is synthesized by reacting ammonia with:
9. Single Superphosphate (SSP): The main phosphate compound in single superphosphate (SSP) is:
10. Triple Superphosphate (TSP): Triple superphosphate is produced by reacting phosphate rock with:
11. Pulp and Paper Industry: The Kraft process in pulp production primarily uses which chemical to digest wood chips?
12. Pulp and Paper Industry: The primary purpose of bleaching in the paper industry is to:
13. Sugar Industry: In sugar production, the clarification of cane juice involves the addition of:
14. Oil and Fats Industry: The process of hydrogenation in the oil and fats industry is used to:
15. Oil and Fats Industry: The main raw material for soap production in the oil and fats industry is:
16. In the Contact Process for sulfuric acid manufacture, vanadium pentoxide is used as a catalyst primarily because:
17. The critical challenge in the production of phosphoric acid via the wet process is:
18. In the chlor-alkali industry, membrane cell technology is preferred over diaphragm and mercury cells due to:
19. In the production of urea from ammonia and CO₂, the unconverted materials are recycled due to:
20. Which of the following best explains the function of formaldehyde in the production of urea-formaldehyde resin?
TYPE : MCQ Intermediate Level (Q.21-Q.25)
21. In pulp and paper industry, the Kraft process is advantageous over sulfite process due to:
22. The saponification number of oil or fat provides an estimate of:
23. In the steam cracking process for ethylene production, the severity of cracking is primarily controlled by:
24. During the polymerization of vinyl chloride to form PVC, the addition of plasticizers results in:
25. The main monomers involved in the production of polyester synthetic fibers are:
- GATE 2026 Chemical Technology-CT: Basics Fundamentals Practice 01
- GATE 2026 Chemical Technology-CT: Basics Fundamentals Practice 02
- GATE 2026 Chemical Technology-CT: Basics Fundamentals Practice 03
- GATE 2026 Chemical Technology-CT: Numerical Based Practice 01
- GATE 2026 Chemical Technology-CT: Numerical Based Practice 02
- GATE 2026 Chemical Technology-CT: Numerical Based Practice 03
Why EII’s Resources Are Essential
- Expert-Curated Content: Questions are meticulously analyzed by EII’s top educators, aligned with the latest GATE syllabus.
- Extensive Mock Tests: Download weekly Mock Test and Practice Sets from your students’ login. Each subject offers 6-8 tests, progressing from basic to advanced levels.
- Proven Success: In GATE 2025, 2024, 2023, 2022, and 2021, numerous questions were directly sourced from EII’s lecture notes and Mock Test Practice papers.
- Free Practice Materials: Download sample papers to strengthen your foundational knowledge across all subjects.
Get Started with Dedicated Practice: Log in to your student account at https://engineersinstitute.com to download the weekly Mock Test and Practice Sets. Practice diligently, as each test includes Detailed Solutions and Analysis Reports with shortcuts, tips, and tricks to master complex topics efficiently.
Historical Question Alignment EII’s resources have consistently reflected GATE exam trends. Here are key topics where questions matched recent years:
- Chemical Reaction Engineering: Direct matches in GATE 2025, 2023, and 2024.
- Mass Transfer: Aligned with GATE 2025, 2022, and 2021.
- Heat Transfer: Similar questions in GATE 2025, 2021, and 2023.
- Process Control: Matches observed in GATE 2025 and 2024.
- Fluid Mechanics: Direct hits in GATE 2025, 2023, and 2022.
- Thermodynamics: Aligned with GATE 2025, 2024, and 2021.
- Plant Design and Economics: Matches in GATE 2025, 2022, and 2023.
- Chemical Technology: Matches in GATE 2025, 2024, and 2023.
- Process Calculations: Matches observed in GATE 2025, 2024, 2022.
- Mechanical Operations: Matches observed in GATE 2025 and 2023.
Tips to Practice Question Papers Effectively
- Simulate Exam Conditions: Time yourself (1.5–2 minutes per question) to build speed.
- Target Weak Areas: Use practice sets to focus on challenging topics.
- Weekly Revision: Revisit solved papers to reinforce concepts.
- Learn from Errors: Analyze mistakes using detailed solutions to improve accuracy.
Benefits of Scheduled Mock Practices
- Enhanced Solving Skills: Regular mocks improve speed and accuracy, vital for the 3-hour GATE exam.
- Reduced Errors: Scheduled practice helps identify and correct mistakes, minimizing errors on exam day.
- Confidence Boost: Familiarity with the format reduces anxiety and builds confidence.
- Performance Insights: Analysis reports guide you to refine your strategy effectively.
Have doubts or technical issues? Contact us at 9990357855 via WhatsApp for instant support!
Get a Call Back
Make your career as Chemical Engineer into the field of government sector as Graduate Trainee, Management Trainee or fresh Engineer and utilise your technical skills for career growth.

